42 dna diagram with labels
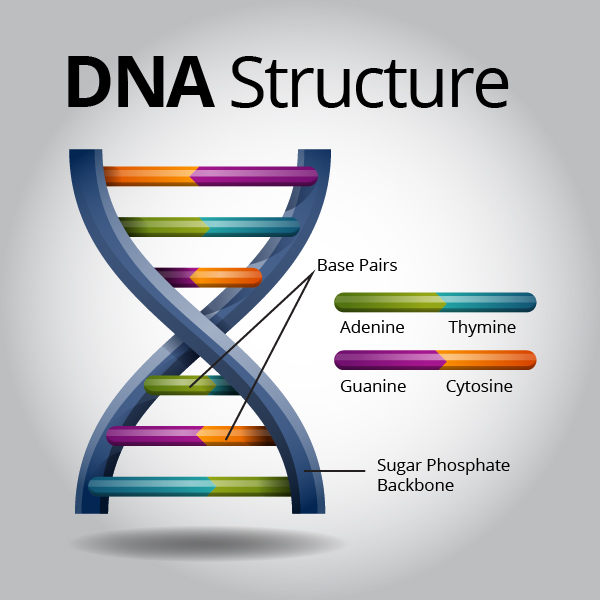
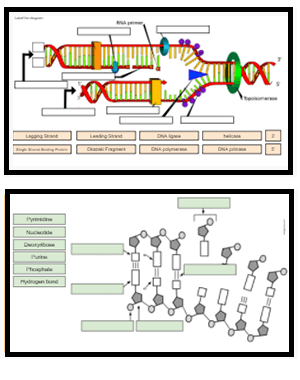
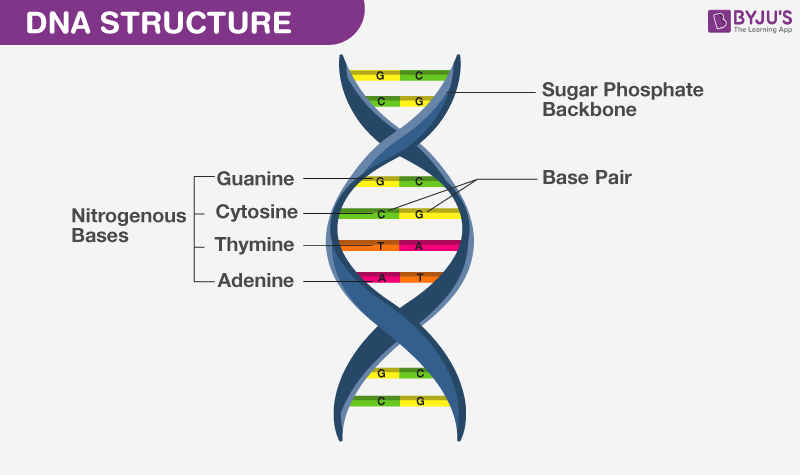
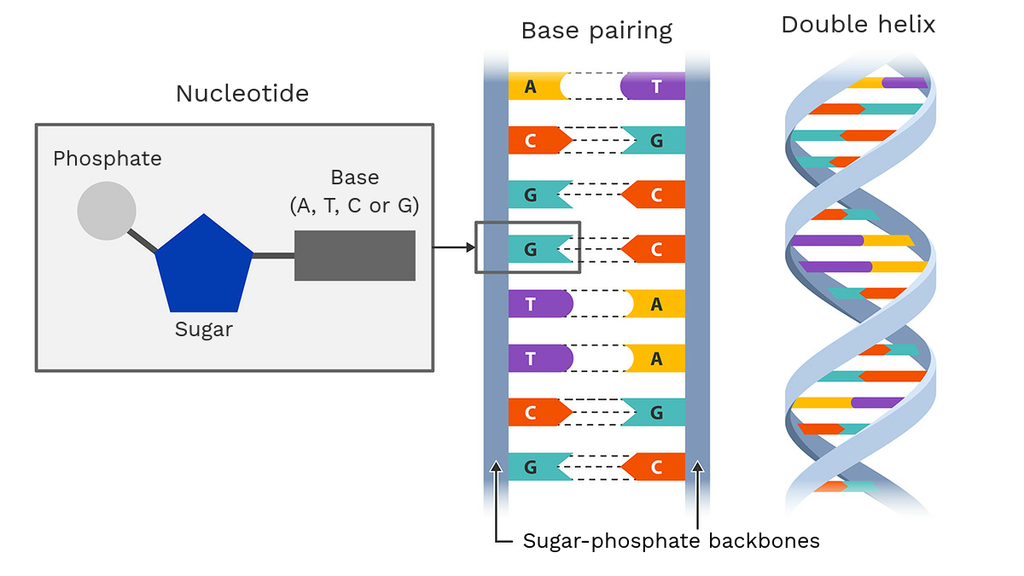
What Is DNA?- Meaning, DNA Types, Structure and Functions - BYJUS The following diagram explains the DNA structure representing the different parts of the DNA. DNA comprises a sugar-phosphate backbone and the nucleotide bases (guanine, cytosine, adenine and thymine). DNA Diagram representing the DNA Structure Read more: Properties of DNA DNA Structure The DNA structure can be thought of as a twisted ladder. Label DNA and Replication - Google Slides Label the diagram: DNA polymerase adds nucleotides (5' to 3') Replication fork is formed. DNA polymerase attaches to the primer. Okazaki fragments bound by ligase. DNA helicase unwinds DNA. Rearrange the steps to indicate the correct order: 1. Enzyme that unwinds DNA.
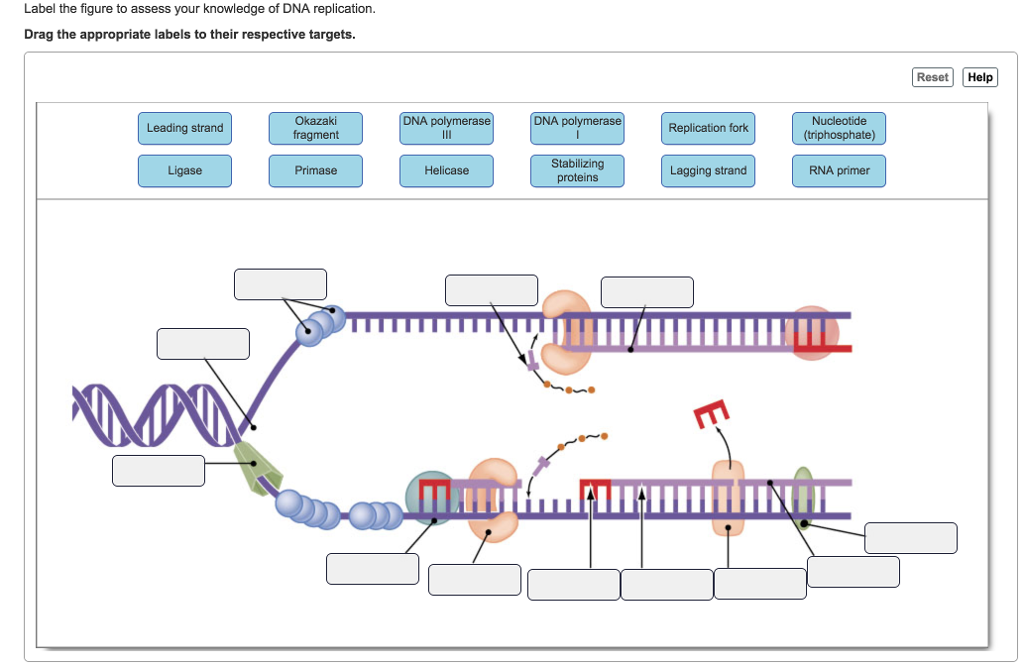
DNA Replication Labeling Diagram | Quizlet The primer synthesized by primase enzyme DNA Polymerase on Leading Strand synthesizes new DNA only in the 5' to 3' direction Ligase An enzyme that connects two fragments of DNA to make a single fragment Lagging Strand The strand in replication that is copied 3' to 5' as Okazaki fragments and then joined up. DNA Polymerase on lagging strand

Dna diagram with labels
Mechanism of DNA Replication (explained with diagrams) | Biology Details of DNA replication can be discussed under the following headings: 1. Activation of deoxyribonucleosides: The four nucleosides of DNA i.e., AMP, GMP, CMP and TMP are found floating free in the nucleus. They all are activated by ATP to form deoxyribonucleoside triphosphatases called ATP, GTP, CTP and TTP. 醫學遺傳學1 - Αποτέλεσμα Google Books Milos Pawlowski, Yavor Mendel, John Kaisermann · ScienceDNA structure: a brief summary Robert Schneidery Rudolf Grosschedl Genes Dev.2007 21: 3027-3043 Alberts, Bruce. Molecular Biology of the Cell; ... DNA - structure - chemguide Joining up lots of these gives you a part of a DNA chain. The diagram below is a bit from the middle of a chain. Notice that the individual bases have been identified by the first letters of the base names. (A = adenine, etc). Notice also that there are two different sizes of base. Adenine and guanine are bigger because they both have two rings.
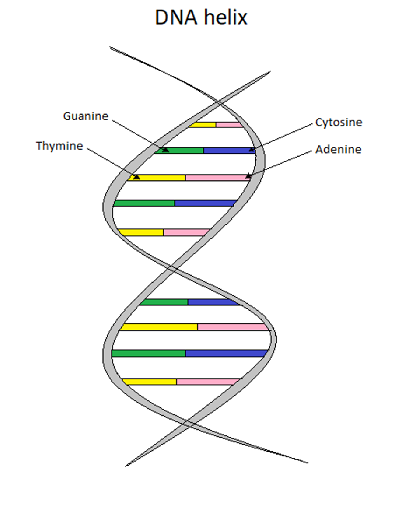
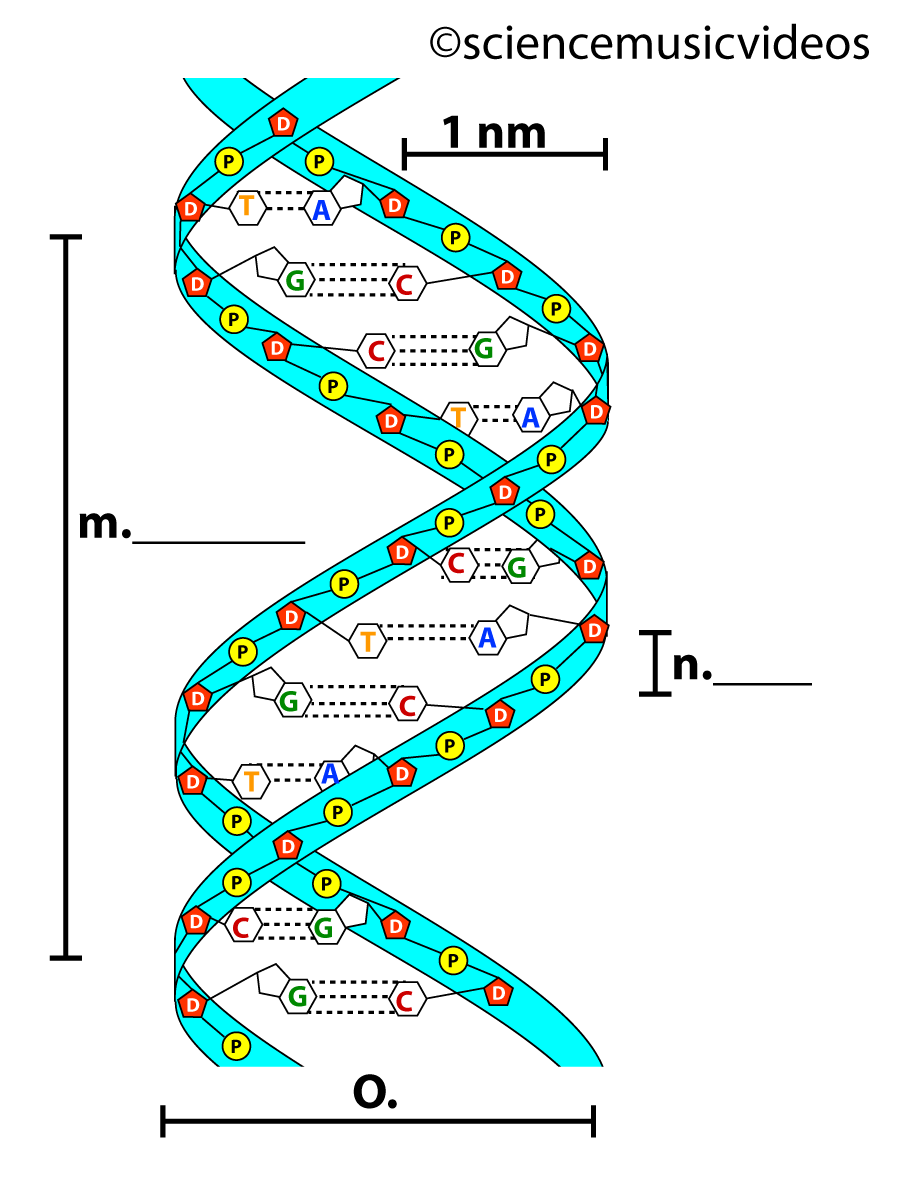
Dna diagram with labels. Isotopic labeling - Wikipedia Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope (an atom with a detectable variation in neutron count) through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell.The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific atoms by their isotope. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the products is measured to determine ... Explain the double helix structure of DNA with a labelled diagram. Explain the double helix structure of DNA with a labelled diagram. Hard Solution Verified by Toppr DNA has a double-stranded helical structure. It was given by Watson and Crick model. It is also known as B form of DNA. It is made up of nitrogenous base, deoxyribose sugar, and phosphate. DNA - Wikipedia DNA is a long polymer made from repeating units called nucleotides, each of which is usually symbolized by a single letter: either A, T, C, or G. The structure of DNA is dynamic along its length, being capable of coiling into tight loops and other shapes. In all species it is composed of two helical chains, bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. ... DNA Structure with Labels - Rae Rocks Teaching DNA Structure with Labels Help your students finally understand DNA structure with labels to help them along the way. Nearly 65% of people are visual learners which make graphics key to engaging students. This no-prep lesson provides all the basics you need to provide students to grasp the structure of DNA. $ 4.99 Add to cart
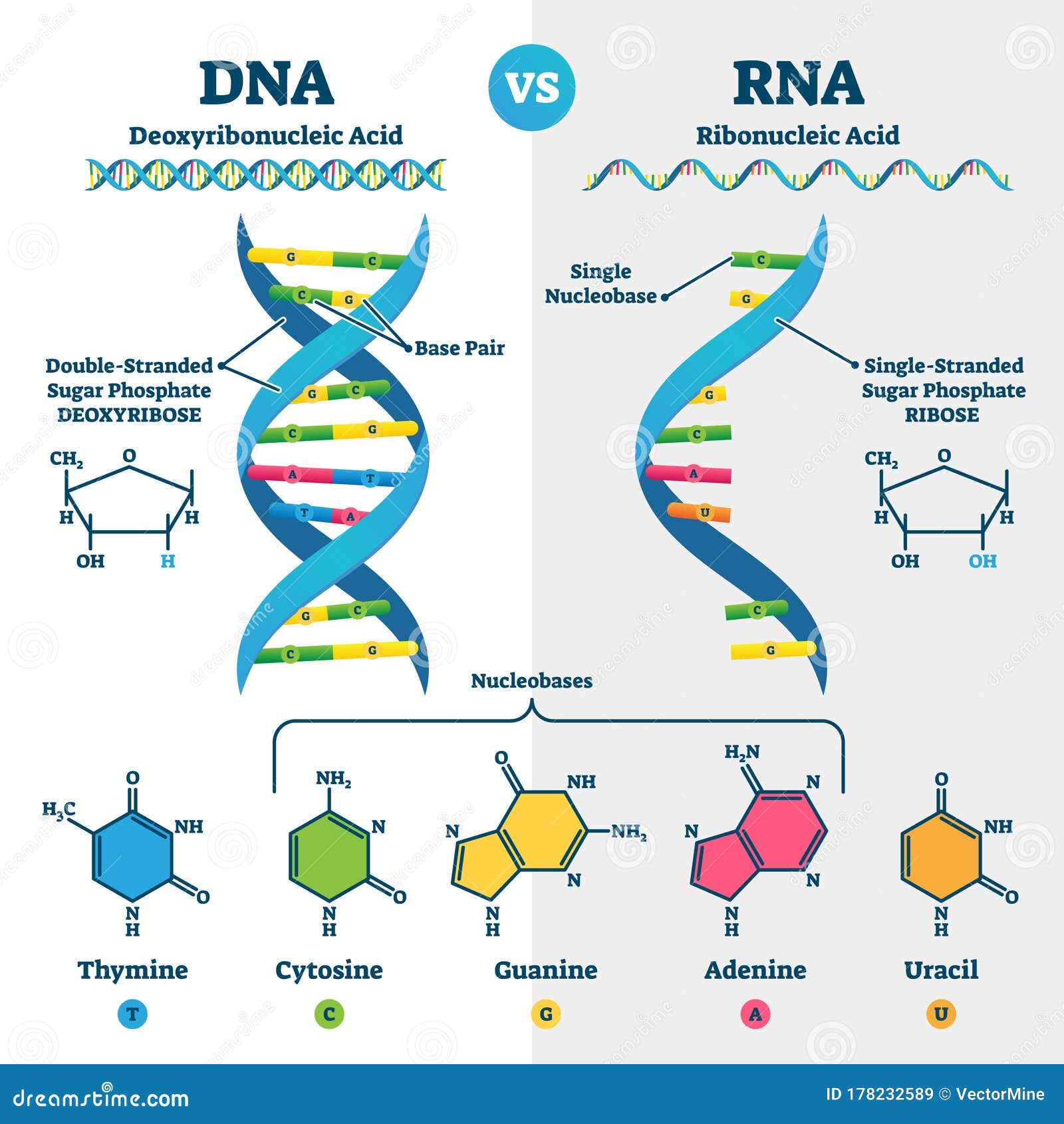
DNA Transcription Diagram: Detailed Explanations - Lambda Geeks Steps shown in the DNA transcription Diagram There are quite a few steps in the process of DNA transcription involved along with involvement of few enzymes as well. There is many function of the DNA that gets involved Initiation considering it as the first step. It is followed by elongation termination, 5' Capping, polyadenylation and splicing. Nucleotide Structure: DNA Diagram | Science Trends The DNA essentially unzips, has the genetic information it carries read, and then reverts back to the double helix form. Ribose And The Difference Between RNA And DNA. While the five-carbon sugar that DNA possesses is called deoxyribose, the five carbon sugar RNA possesses is just called ribose. Ribose is necessary for the formation of molecules utilized to transfer energy between different portions of a cell. frontlinegenomics.com › dna-sequencing-how-toDNA Sequencing: How to Choose the Right Technology Aug 06, 2021 · The DNA sequencing landscape. The global market for DNA sequencing is predicted to grow from $15.7 billion in 2021 to $37.7 billion by 2026. The rising prevalence of viral diseases, such as COVID-19, and the increasing cases of cancer globally are likely to drive genomic research and propel the industry at an even more rapid rate. en.wikipedia.org › wiki › BiotechnologyBiotechnology - Wikipedia Pharmacogenomics (a combination of pharmacology and genomics) is the technology that analyses how genetic makeup affects an individual's response to drugs. Researchers in the field investigate the influence of genetic variation on drug responses in patients by correlating gene expression or single-nucleotide polymorphisms with a drug's efficacy or toxicity.
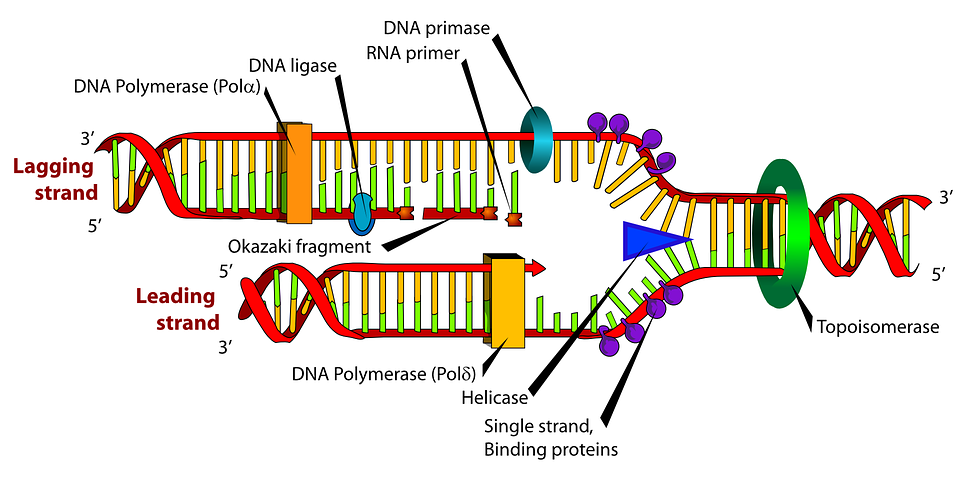
dna-labeling | NEB A variety of enzymatic or chemical methods are available to generate nucleic acids labeled with radioactive phosphates, fluorophores, or nucleotides modified with biotin or digoxygenin for example. Nucleic acids may be labeled at their 5´ end, their 3´ end, or throughout the molecule depending on the application. DNA Replication (With Diagram) | Molecular Biology The DNA polymerase acts on dATP, dGTP, dCTP, dTTP. These new nucleotides are added one-by-one at 3′-OH end of the growing strand. DNA polymerase needs a primer to synthesize new strand. Small RNA primer hydrogen bonds with the template. This primer provides free 3′- OH end to add new nucleotides. DNA synthesis takes place in 5′ → 3′ direction. Methods for Labeling Nucleic Acids - Thermo Fisher Scientific A linear DNA template with this promoter sequence can be used with T7 RNA polymerase to in vitro transcribe labeled RNA probes. The +1 position indicates the first nucleotide that is incorporated into the RNA during transcription. The bases at positions +1 through +3 are critical for transcription and must be G and 2 purine bases, respectively. DNA Molecule Label Diagram | Quizlet Molecule found on the side of a DNA molecule. Double Helix. two strands of nucleotides wound about each other; structure of DNA. Thymine. the nucleotide that hydrogen bonds with the nucleotide adenine in DNA. Adenine. the nucleotide that hydrogen bonds with the nucleotide thymine in DNA or with uracil in RNA. Guamine.
4 Ways to Use DNA Helix Diagrams in PowerPoint DNA diagram is a graphical chart resembling the shape of a double helix, a symbol of the human DNA structure that defines the characteristics of a person. This metaphor is used to illustrate an organizational culture of a corporation or smaller company, its underlying values and principles. The DNA helix diagram can also be used while comparing ...
DNA Replication Process with Diagrams Class 12 - BYJUS The two strands of DNA unwind at the origin of replication. Helicase opens the DNA and replication forks are formed. The DNA is coated by the single-strand binding proteins around the replication fork to prevent rewinding of DNA. Topoisomerase prevents the supercoiling of DNA. RNA primers are synthesised by primase.
Replication Fork: Definition, Structure, Diagram, & Function The replication fork is a structure which is formed during the process of DNA replication. It is activated by helicases, which helps in breaking the hydrogen bonds, and holds the two strands of the helix. The resulting structure has two branching's which is known as prongs, where each one is made up of single strand of DNA.
assignmentessays.comAssignment Essays - Best Custom Writing Services Get 24⁄7 customer support help when you place a homework help service order with us. We will guide you on how to place your essay help, proofreading and editing your draft – fixing the grammar, spelling, or formatting of your paper easily and cheaply.
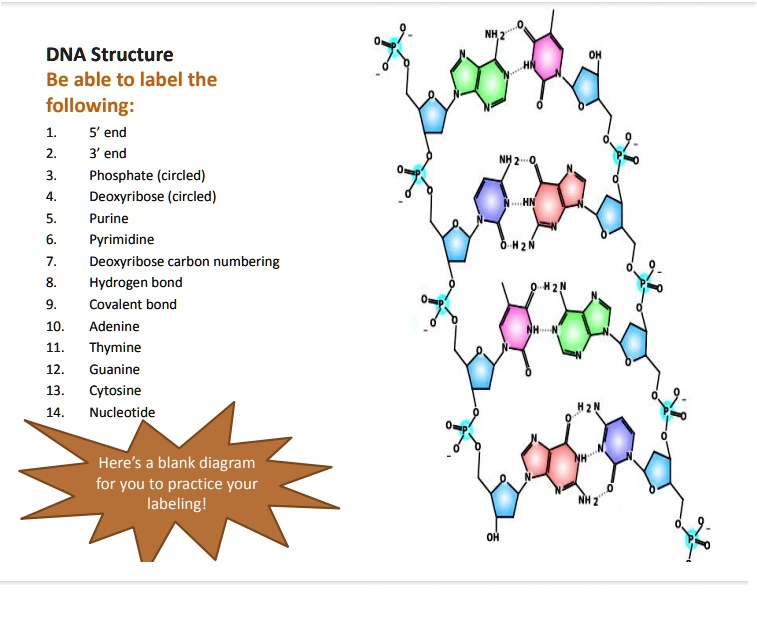
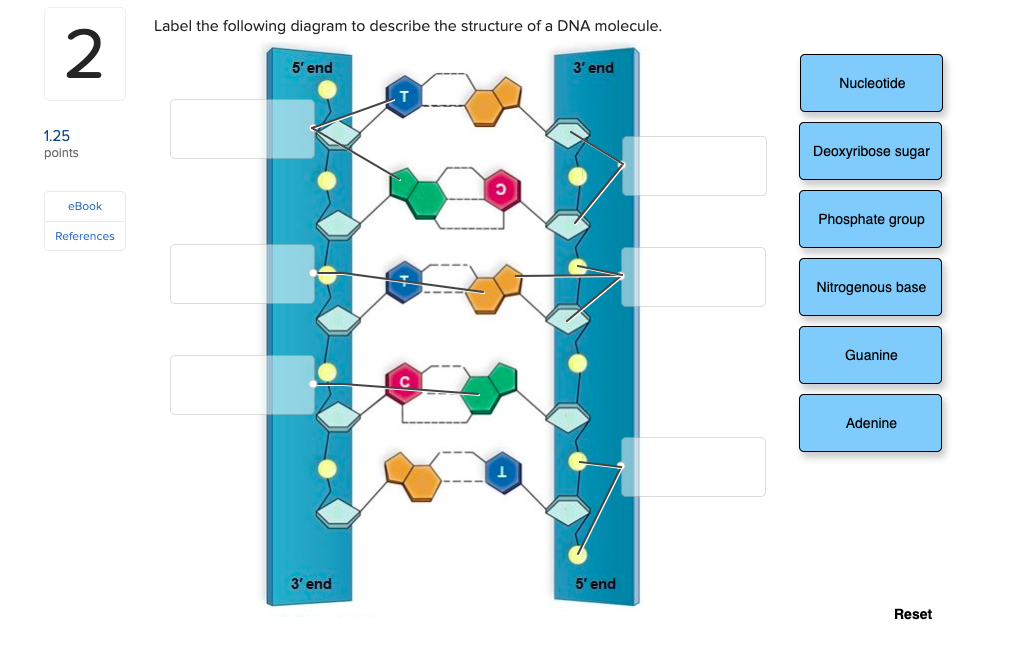
PDF DNA Structure Worksheet - Commack Schools 11. Write the complementary sequence to following DNA strand: 12. Use the image at the right to complete the follow: Circle a nucleotide. Label the sugar and phosphate. Label the bases that are not already labeled 13. On the Following Page, color the DNA structure.
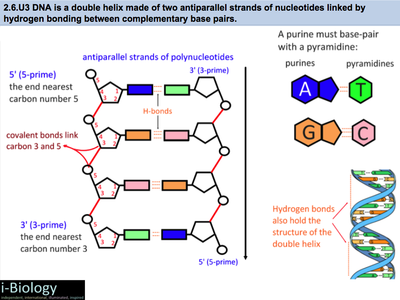
Structure Of DNA | Function, Summary, Diagram & Model - A Level Biology It is called double helix because, in the three-dimensional model, DNA molecule was seen to have a spiral or helical structure made up of two polynucleotide chains. This helical structure was made when the two polynucleotide chains are wound around each other. 3. The polynucleotide chains are coiled anti-parallel.
› scitable › topicpageFluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH) | Learn Science at ... (a) The basic elements of FISH are a DNA probe and a target sequence. (b) Before hybridization, the DNA probe is labeled by various means, such as nick translation, random primed labeling, and PCR.
› lifestyleLifestyle | Daily Life | News | The Sydney Morning Herald The latest Lifestyle | Daily Life news, tips, opinion and advice from The Sydney Morning Herald covering life and relationships, beauty, fashion, health & wellbeing
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Flow_cytometryFlow cytometry - Wikipedia This method could theoretically allow the use of 40 to 60 distinguishable labels and has been demonstrated for 30 labels. Mass cytometry is fundamentally different from flow cytometry: cells are introduced into a plasma, ionized, and associated isotopes are quantified via time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Although this method permits the use of ...
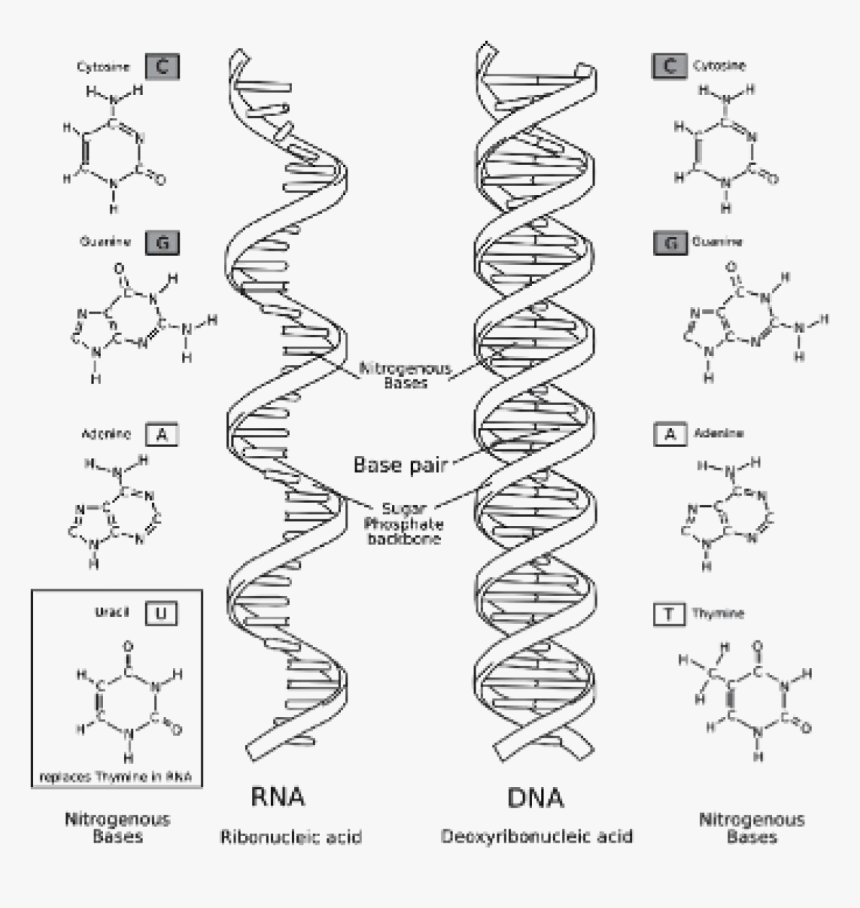
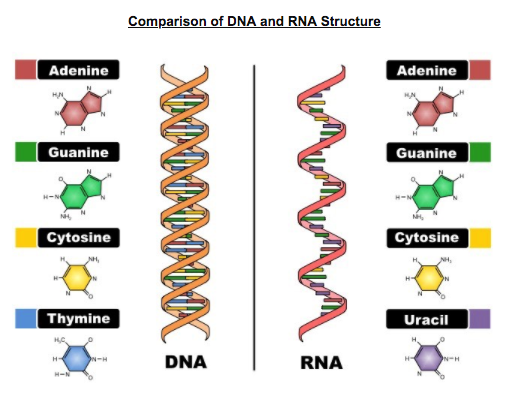
DNA vs RNA - Difference and Comparison | Diffen DNA is found in the nucleus of a cell (nuclear DNA) and in mitochondria (mitochondrial DNA).It has two nucleotide strands which consist of its phosphate group, five-carbon sugar (the stable 2-deoxyribose), and four nitrogen-containing nucleobases: adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine.. During transcription, RNA, a single-stranded, linear molecule, is formed.
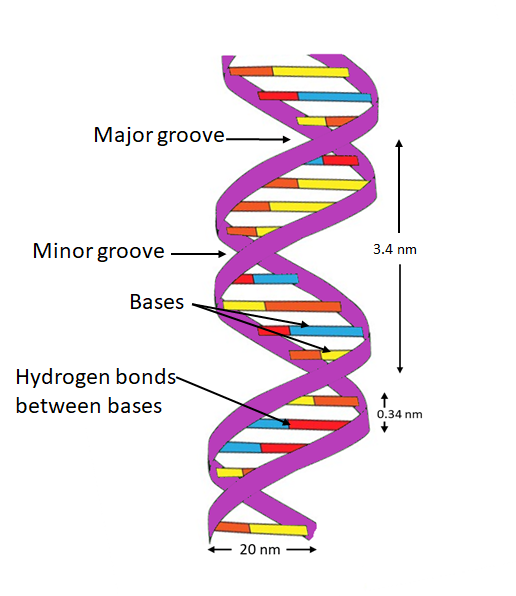
DNA: Structure, Forms and Functions (With Diagram) - Biology Discussion To recall the helix geometry of B-form DNA, it is described once again: 1. The diameter of the helix is 20 A 0. 2. The pitch, i.e., the length of helix needed to complete one turn, is 34 A 0. 3. The distance between two base pairs is 3.4 A 0. 4. In the physiologic solution, there are about 10.5 base pairs in one pitch rather than 10.0 found in fibre. 6.
nap.nationalacademies.org › read › 13165Reading: A Framework for K-12 Science Education: Practices ... Science, engineering, and technology permeate nearly every facet of modern life and hold the key to solving many of humanity's most pressing current and future challenges. The United States' position in the global economy is declining, in part because U.S. workers lack fundamental knowledge in these fields. To address the critical issues of U.S. competitiveness and to better prepare the ...
DNA Transcription | Definition, Stages & Diagram - iBiologia DNA Transcription | Definition, Stages & Diagram DNA Transcription DNA Transcription Introduction: In DNA transcription, the DNA sequence of a gene is copied out (transcribed) in order to make a molecule of RNA. It is the first step in the expression of the gene. The process of DNA Transcription is done by the enzymes known as RNA polymerases.
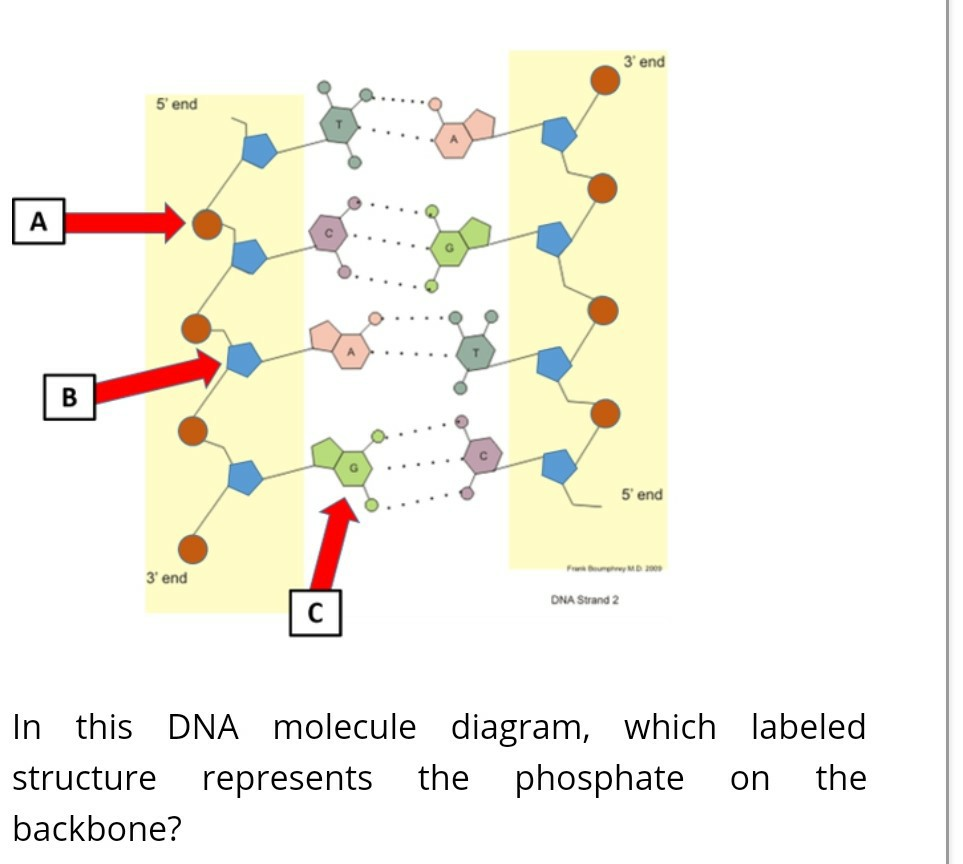
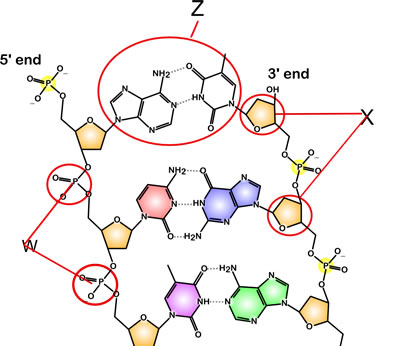
Solved The diagram depicts the general structure of DNA, | Chegg.com The diagram depicts the general structure of DNA, with a single nucleotide circled. Label the diagram with the names of the three components of a nucleotide Anwer Bank nitrogenous base phosphate group deutytibes Question: The diagram depicts the general structure of DNA, with a single nucleotide circled.
Solved The diagram depicts the molecular structure of DNA ... - Chegg Expert Answer 100% (32 ratings) 1- Pyramidine base. 2 - Purine base. 3 - … View the full answer Transcribed image text: The diagram depicts the molecular structure of DNA. Label the diagram with the names of the components of the nucleic acid HO Aner Bank pyrimidi P-O phosphate hicho hydrogen bond PO Previous question Next question
3.3.5 Draw a simple diagram of DNA structure - YouTube 3.3.5 Draw and label a simple diagram of the molecular structure of DNA. Here I demonstrate drawing the structure of DNA. You don't need to be an artist, its relative positions of the phosphate...
drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the components of ... Diagram dna identify onto drag labels strands replicating components crispr pfam assoc. Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the components of. Category: Diagrams. Post navigation. Previous post: john deere 48 inch mower deck belt diagram Deck mower 54a accel deere 54 x500 john tractor x580 x590 48 x380 series inch deep x570 lawn ...
DNA function & structure (with diagram) (article) | Khan Academy DNA structure and function DNA is the information molecule. It stores instructions for making other large molecules, called proteins. These instructions are stored inside each of your cells, distributed among 46 long structures called chromosomes. These chromosomes are made up of thousands of shorter segments of DNA, called genes.
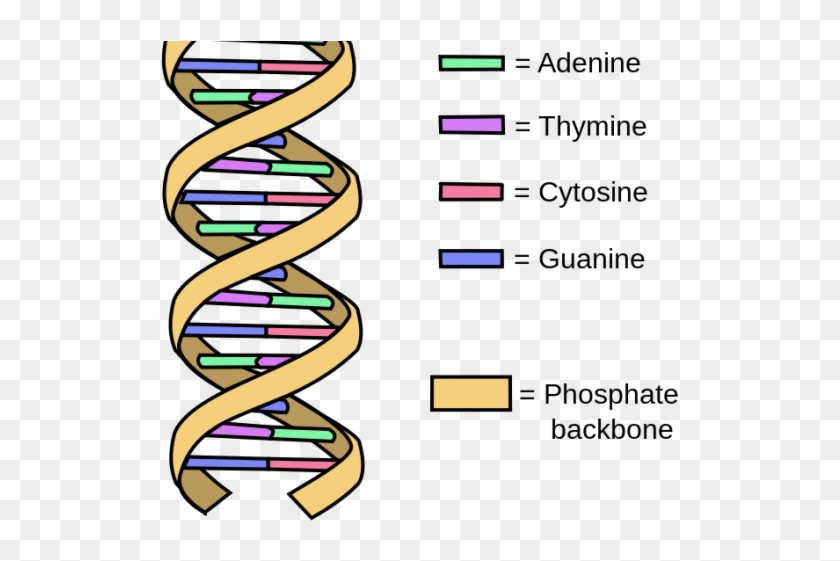
The Structure of DNA - University of Arizona The DNA molecule actually consists of two such chains that spiral around an imaginary axis to form a double helix (spiral.) Nucleic acid molecules are incredibly complex, containing the code that guarantees the accurate ordering of the 20 amino acids in all proteins made by living cells. ... This figure is a diagram of a short stretch of a DNA ...
DNA - structure - chemguide Joining up lots of these gives you a part of a DNA chain. The diagram below is a bit from the middle of a chain. Notice that the individual bases have been identified by the first letters of the base names. (A = adenine, etc). Notice also that there are two different sizes of base. Adenine and guanine are bigger because they both have two rings.
醫學遺傳學1 - Αποτέλεσμα Google Books Milos Pawlowski, Yavor Mendel, John Kaisermann · ScienceDNA structure: a brief summary Robert Schneidery Rudolf Grosschedl Genes Dev.2007 21: 3027-3043 Alberts, Bruce. Molecular Biology of the Cell; ...
Mechanism of DNA Replication (explained with diagrams) | Biology Details of DNA replication can be discussed under the following headings: 1. Activation of deoxyribonucleosides: The four nucleosides of DNA i.e., AMP, GMP, CMP and TMP are found floating free in the nucleus. They all are activated by ATP to form deoxyribonucleoside triphosphatases called ATP, GTP, CTP and TTP.

















Post a Comment for "42 dna diagram with labels"